
This work,
NaVILA, is proposed by Cheng et al. and presents a vision-language action (VLA) model for legged robot navigation.
Please refer to their
website for more details.
We demonstrate its deployment on a Unitree A1 quadruped performing indoor tasks.
The VLA model is executed on an RTX 5090 server, with communication handled via UDP.
A detailed setup guide is provided for RTX 50-series GPUs and newer Ubuntu environments.

We present a feasibility-guided planning framework that enables coordinated navigation across complex terrains through multiple specialized locomotion policies.
Our contribution focuses on the joint training paradigm while maintaining interpretable policy selection and supporting integration of new locomotion skills without retraining.
The planning system achieved a 98.60% success rate in simulation and 70% in the real world on mixed terrain.
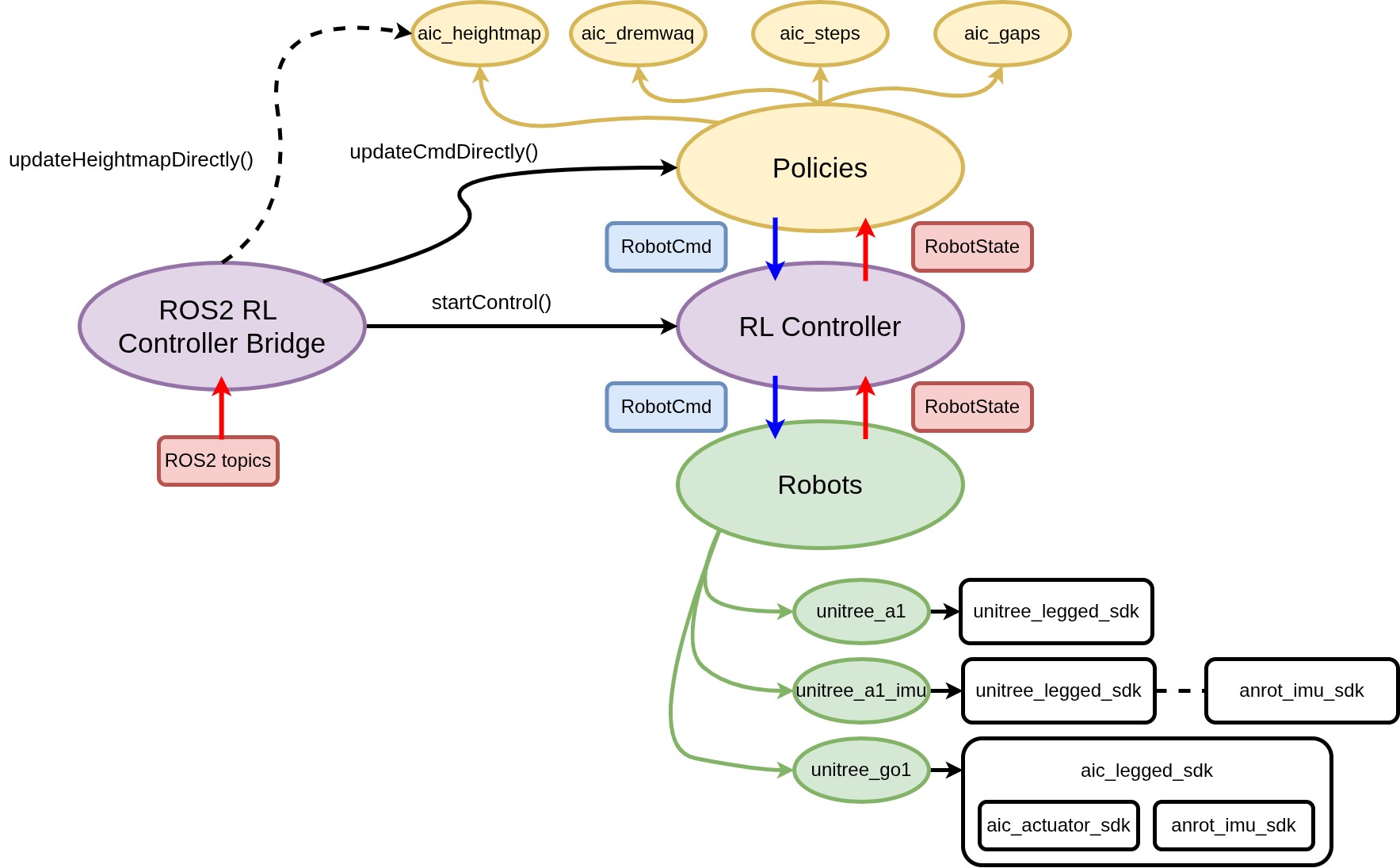
Building up quadruped robot interface for customized actuators and sensors through LCM communication.
Training locomotion policy from IsaacGym and IsaacLab. C++ deployment and parameters (action scales, motor gains) fine-tuning.
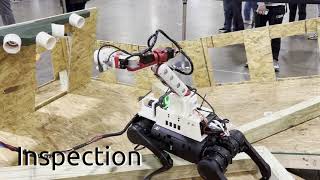
Navigation deployment from our research: Feasibility-Guided Planning over Multi-Specialized Locomotion Policies.
ROS2 integration on navigation, locomotion, manipulator teleoperation and image detection.
Successfully traversed multiple extreme terrain autonomously.
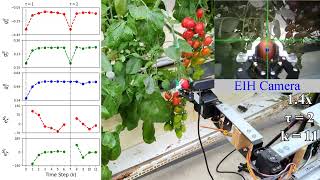
This paper presents a self-built tomato harvesting robot with dual-camera IBVS algorithm implemented to solve the dislocation problem.
In the greenhouse experiment, the harvesting time is reduced from 21.2 to 6.26 seconds by the cumulative error compensation,
and the success rate for picking tomatoes is 68.4%.




